Understanding Sacral Dysfunction: A Comprehensive Examination

Intro
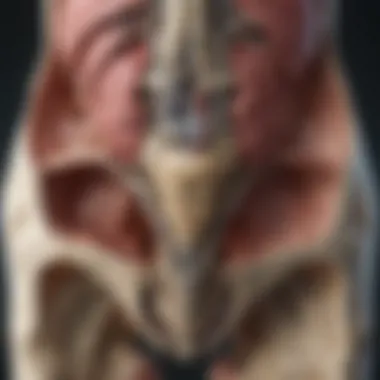
Sacral dysfunction is an often overlooked yet significant condition that can influence various aspects of a person's health. The sacrum, located at the base of the spine, plays a crucial role in the structure and function of the pelvis, spine, and overall musculoskeletal system. When dysfunction occurs in this area, it can lead to a multitude of symptoms and impact other bodily systems.
This examination aims to provide an in-depth understanding of sacral dysfunction, covering its causes, symptoms, and potential treatments. We will also explore the anatomical and physiological aspects that contribute to this condition. Highlighting recent research and case studies will further illustrate the importance of recognizing and addressing sacral health, ultimately empowering students, researchers, and healthcare professionals with knowledge on this vital topic.
Research Overview
Summary of Key Findings
Research indicates that sacral dysfunction can arise from various underlying factors such as trauma, poor posture, repetitive movements, and even emotional stress. These factors can lead to a misalignment or dysfunction of the sacroiliac joint, contributing to pain and restricted movement in the lumbar spine and pelvis. A detailed review of case studies supports the notion that treatment approaches incorporating physical therapies, along with lifestyle adjustments, significantly improve patient outcomes.
"Understanding sacral dysfunction is vital for holistic health, as it can affect not just the back and pelvis, but also the entire body system through pain and compensatory mechanisms."
Research Objectives and Hypotheses
The primary objective of this research is to delineate the factors contributing to sacral dysfunction and explore their implications for overall health. We hypothesize that a comprehensive approach to diagnosing and treating sacral dysfunction will enhance patient recovery and quality of life. By emphasizing the interconnectedness of the sacral region with other bodily systems, we aim to provide a broader perspective on health that goes beyond isolated treatments.
Methodology
Study Design and Approach
This study employs a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative data from clinical trials with qualitative insights from patient interviews. This strategy provides a more complete picture of sacral dysfunction and how it can be effectively managed.
Data Collection Techniques
Data was gathered through literature review, clinical assessments, and patient surveys. The literature includes peer-reviewed articles and recent clinical studies focusing on sacral dysfunction. Clinical assessments involved standardized tests to evaluate the range of motion, strength, and pain levels in patients. Patient surveys collected firsthand accounts of symptoms and treatment experiences, enriching the data pool with personal narratives.
Through this comprehensive examination, we aim to serve as a vital resource for individuals seeking to understand sacral dysfunction in a detailed manner, shedding light on its various dimensions and the importance of maintaining sacral health.
Preface to Sacral Dysfunction
The sacrum plays a critical role in the structure and function of the human body. Understanding sacral dysfunction is essential for various professionals in health and wellness. This section will discuss its importance, providing insights into the definition, historical context, and its far-reaching implications for overall health. Sacral dysfunction can affect mobility, stability, and even visceral function, linking it directly to an individual's quality of life. By examining this topic, we can highlight the interconnected nature of musculoskeletal and neurological health, ultimately guiding effective treatment strategies.
Definition and Relevance
Sacral dysfunction refers to a range of issues related to the sacrum, a triangular bone at the base of the spine. This condition may encompass disc herniation, abnormalities in alignment, or muscle dysfunction affecting the surrounding structures. Its relevance lies in the increasing recognition of how sacral health impacts not only mobility but also organ function and pain perception. Experts highlight that dysfunction in this area can manifest as chronic pain, altered gait, and even reproductive health issues.
Given the sacrum's position, it serves as a keystone in the body’s structure. Dysfunction can lead to a cascading effect on pelvic stability and posture, directly impacting foundational movements. Therefore, understanding this dysfunction aids healthcare providers in understanding patient complaints that might otherwise seem unrelated.
Historical Context
The study of sacral dysfunction has evolved significantly over centuries. Early anatomical studies recognized the sacrum's importance in the spine's structure, but it was not until the 20th century that focused research began. Initially, sacral pathology was often overlooked in favor of more prominent areas such as the cervical and lumbar regions.
With the advent of modern imaging techniques in the late 20th century, such as MRI and CT scans, a clearer understanding of sacral issues emerged. These advancements revealed that many patients with chronic pain syndromes had underlying sacral dysfunctions. Current literature emphasizes the need to consider the sacrum as a vital component of the spinal system.
"The sacrum is not just a bone; it is a complex structure that plays a critical role in human biomechanics and overall health."
As research continues to unfold, the integration of functional assessments and treatment modalities has gained traction. Today, health professionals, including physiotherapists, chiropractors, and osteopaths, are increasingly aware of how sacral dysfunction can cause a wide array of symptoms that extend beyond simple back pain.
Anatomy of the Sacrum
The anatomy of the sacrum is crucial in understanding sacral dysfunction. The sacrum plays a significant role in the overall biomechanical stability of the pelvis and spine. Without a clear comprehension of its structure and relations, one cannot fully grasp the complexities of dysfunctions that may arise. Proper function of the sacrum influences not only local pain but also affects wider muscular and skeletal alignment.
Sacral Structure
The sacrum is a large, triangular bone, located at the base of the spine, connecting the pelvis with the vertebral column. It consists of five fused vertebrae, labeled S1 to S5. Each sacral segment contributes to its unique anatomical shape and mechanical function. The sacrum has several critical landmarks, including the sacral promontory, which marks the anterior edge of the first sacral vertebra.
Understanding the shape and relation of the sacrum to the spine is vital. The sacrum supports the weight of the upper body when sitting and standing. Additionally, it forms the posterior wall of the pelvis, creating a bony boundary essential for protecting pelvic organs. Any deviations in sacral alignment can lead to chronic pain or impairments.
Key components of the sacral structure include:
- Alae: Wing-like projections on either side that articulate with the ilium of the pelvis.
- Foramina: Holes in the sacrum through which nerves and blood vessels pass, contributing to neurological function in the lower extremities.
- Sacral Canal: A continuation of the vertebral canal that houses the cauda equina, a crucial structure for lower limb nerve supply.
Surrounding Musculoskeletal Relations
The sacrum interacts complexly with surrounding muscular and skeletal structures. It provides attachment points for many muscles and ligaments. The close relationship between surrounding muscles, like the gluteus maximus and iliopsoas, means dysfunction in the sacrum can result in muscle tightness or weakness, leading to functional impairment.
Moreover, the sacroiliac joints, where the sacrum meets the iliac bones of the pelvis, are critical in transferring weight from the upper body to the legs. Dysfunction in these joints can cause significant pain and limit mobility. Recognizing how the sacrum relates to adjacent structures, including the lumbar spine and the hip joints, is essential in diagnosing and treating sacral dysfunction.
Proper function of the sacrum influences local pain and wider muscular alignment. It is an area of focus when investigating musculoskeletal problems.
In summary, an in-depth understanding of the sacral anatomy highlights its importance in overall health. By addressing both the structure and its relations with surrounding tissues, healthcare practitioners can better manage sacral dysfunction, enhancing patients' quality of life.
Physiology of Sacral Function
The physiology of sacral function plays a critical role in understanding how the sacrum interacts with various bodily systems. The sacrum is not merely a bony structure; it serves as a vital hub linking the central nervous system to the pelvic region. Recognizing this interplay helps in identifying dysfunctions that can arise from an imbalance in this complex system. The physiological aspects connected to the sacrum impact movement, stability, and overall health.


Nervous System Connections
The nervous system connections associated with the sacrum are fundamentally important. Specifically, the sacral region is innervated by the sacral plexus, which is a network of nerves that includes contributions from the L4 to S4 spinal nerves. These neural pathways control key functions in the lower body, including motor control and sensory feedback. For instance, dysfunction in these nerves can lead to symptoms like lower back pain, sciatica, or bladder dysfunction.
Several benefits emerge from understanding these connections. Firstly, by mapping how the sacral nerves influence muscle activation in the pelvic floor, therapists can design targeted interventions for patients experiencing pelvic pain or dysfunction. Furthermore, knowledge of these neural pathways allows healthcare providers to identify potential sources of chronic pain more effectively. Understanding which nerves affect various regions is also crucial for surgical interventions.
Interplay with Pelvic Structures
The interplay between the sacrum and surrounding pelvic structures is such that it impacts stability and movement in the lower body. The sacrum serves as a keystone, articulating with the ilium at the sacroiliac joint. This relationship is essential for weight distribution and shock absorption during activities like walking and running. Any dysfunction in this region can lead to compensatory mechanisms that may overstrain other joints, resulting in pain and dysfunction throughout the kinetic chain.
Consider the muscles attached to this area, such as the gluteus maximus and piriformis. Their functions are intricately linked to sacral positioning and movement. Training and rehabilitation strategies often focus on optimizing this relationship. For example, exercises designed to strengthen the gluteal muscles can directly enhance sacral stability, improving overall mobility.
Maintaining the health of these structures is paramount in preventing chronic conditions associated with sacral dysfunction. As a result, rehabilitation efforts that incorporate an awareness of this interplay will focus on balance, flexibility, and strength in these crucial areas.
Important Note: The health of the sacral region and its connections to the pelvic structures cannot be underestimated, as they influence the efficiency of the entire lower body framework.
In summary, a clear understanding of the physiology of sacral function provides a foundation for addressing various aspects of sacral health. It forms the backbone for devising effective diagnostic and treatment protocols in the context of sacral dysfunction.
Common Causes of Sacral Dysfunction
Understanding the common causes of sacral dysfunction is crucial for identifying and treating this condition properly. Sacral dysfunction can have far-reaching impacts on mobility, comfort, and overall health. By recognizing the specific elements that lead to dysfunction, clinicians and patients can work together to prevent, manage, or mitigate the associated symptoms. The importance of determining these causes lies in its direct influence on treatment approaches, which can vary significantly based on the underlying issues.
Some causal factors are more apparent than others, and they often require careful investigation to ensure a comprehensive assessment.
Trauma and Injury
Trauma and injury represent one of the leading causes of sacral dysfunction. This may include accidents, falls, or sports injuries. The sacrum can be affected by direct impacts or indirect forces transmitted through the pelvis. Following an injury, patients might experience pain or a reduced range of motion.
Injuries may not always be easily detectable, especially in cases where soft tissue damage occurs alongside structural impact.
Physical examination and imaging modalities can reveal hidden soft tissue injuries or fractures, which may not always present obvious symptoms initially. For example, stress fractures or ligament sprains are often overlooked but can cause significant dysfunction if not addressed.
Postural Issues
Postural issues are another critical factor contributing to sacral dysfunction. Everyday habits, including how one sits, stands, or moves, can significantly impact the sacral region. Prolonged periods of poor posture lead to uneven stress distribution across pelvic structures.
Common postural challenges include:
- Slouching while sitting.
- Overextending the lower back.
- Carrying uneven loads.
These behaviors can result in muscle imbalances that place additional strain on the sacrum, resulting in discomfort or dysfunction over time. Recognizing and correcting these postural deficiencies is important to prevent long-term issues. Professional guidance, such as from physical therapists, may be needed to develop effective strategies for better posture.
Chronic Conditions
Chronic conditions may also play a significant role in sacral dysfunction. Issues such as arthritis or degenerative disc disease can lead to prolonged inflammation or compression in the sacral area.
Conditions to consider include:
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of cartilage can affect the sacrum's movement.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: A type of chronic inflammation affecting the spine and sacroiliac joints.
- Fibromyalgia: Can amplify pain perception in the sacral region.
These conditions can result in complex pain patterns and may require multi-dimensional treatment strategies. Addressing these underlying chronic issues becomes essential in managing sacral dysfunction effectively.
Symptoms Associated with Sacral Dysfunction
Understanding the symptoms linked to sacral dysfunction is crucial for diagnosing and managing the condition effectively. The clinical presentation often provides foundational insights into the dysfunction. Sacral dysfunction can manifest in various ways, profoundly affecting patients' quality of life. Additionally, recognizing these symptoms allows healthcare professionals to tailor treatment plans to alleviate discomfort and improve functionality.
Pain Manifestations
Pain is often the first noticeable symptom when it comes to sacral dysfunction. Patients may experience localized discomfort in the lower back or buttocks region. This pain can vary in intensity, ranging from mild to severe, and may radiate to nearby areas such as the hips or thighs.
Common characteristics of pain manifestations include:
- Aching: Many patients report a persistent dull ache, which can become more pronounced during physical activities.
- Sharp Pain: Some individuals may experience acute pain, particularly when sitting for extended periods or transitioning from sitting to standing.
- Cramping: This symptom may occur, especially during movement or exercise, and can indicate muscle tension associated with the dysfunction.
It is important to note that the pain resulting from sacral dysfunction can significantly limit mobility and impact daily activities. Effective management often involves a combination of pain relief strategies, including physical therapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustments.
Neurological Symptoms
Sacral dysfunction can also lead to neurological symptoms, indicating that the nerves surrounding the sacrum may be affected. These symptoms provide insight into the severity of the dysfunction and suggest potential nerve compression or irritation. Common neurological symptoms include:
- Numbness and Tingling: Patients may experience sensations of tingling or numbness in the lower extremities or the perineal area. This symptom often correlates with nerve involvement in the sacral region.
- Weakness: Some individuals may notice weakness in their legs or pelvic floor muscles. This weakness can complicate mobility and lead to difficulties in maintaining balance.
- Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction: In some cases, sacral dysfunction can disrupt normal bowel and bladder functions, leading to urgency, incontinence, or retention issues.
Prompt recognition and assessment of these symptoms can guide clinicians in establishing an accurate diagnosis and formulating effective treatment strategies tailored to individual needs.
Functional Impairments
Functional impairments resulting from sacral dysfunction can be profound. Patients may find it challenging to perform routine activities due to discomfort and reduced mobility. Impairments can be categorized as follows:
- Restricted Range of Motion: Patients often struggle with flexibility, which can limit participation in both recreational and daily activities.
- Difficulty with Movement: Simple movements like bending or lifting may become challenging, sometimes exacerbating the pain.
- Altered Gait: Changes in walking patterns may occur as individuals adapt to minimize discomfort, leading to potential cascading effects on the hips, knees, and lower back.

These functional challenges highlight the importance of addressing sacral dysfunction comprehensively. Effective intervention strategies should focus not only on alleviating pain but also on enhancing overall functional capabilities. A multidisciplinary approach might include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and ergonomic adjustments designed to accommodate the specific needs of the patient.
Diagnostic Approaches
Diagnostic approaches are critical in understanding sacral dysfunction. This stage of evaluation provides a clear framework for identifying the condition, which is often complex in nature. A systematic diagnostic process aids healthcare professionals in distinguishing between sacral dysfunction and other ailments that might present similar symptoms. This importance amplifies in cases where early intervention can significantly alter the course of treatment and patient recovery.
Clinical Assessment Techniques
Clinical assessment techniques are often the first line of evaluation. These methods encompass thorough patient history taking and physical examinations. During the history phase, doctors gather detailed information about the patient’s symptoms, duration, and any factors that may exacerbate or relieve discomfort. The physical examination typically incorporates a functional assessment to evaluate mobility and pain response.
Palpation of the sacral area is essential in this assessment. It helps identify tenderness, asymmetries, or muscle tension around the sacrum and surrounding structures. Additionally, specialized tests like the sacroiliac joint stress test may be conducted to confirm exhaustion of standard evaluations. This methodical approach ensures that every relevant detail is captured, thus offering a foundation for further investigative procedures.
Imaging Modalities
Imaging modalities play a significant role in diagnosing sacral dysfunction, providing visual information that complements clinical assessments. Commonly used techniques include X-rays, MRI, and CT scans.
- X-rays can display structural abnormalities, such as fractures or deviations in the sacrum.
- MRI is particularly useful for examining soft tissue and nerve structures, allowing for a clear view of any pressures on nerves related to sacral injuries.
- CT scans offer detailed cross-sectional images and can reveal complex fractures or other detailed structural issues.
Each imaging technique comes with its unique benefits, making it vital for healthcare providers to select the appropriate modality based on the specific clinical scenario and presenting symptoms.
Differential Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis involves distinguishing sacral dysfunction from other conditions that may mimic its symptoms. This step is crucial for formulating an effective treatment plan. Conditions such as radiculopathy, herniated disks, or even pelvic inflammatory diseases can produce similar pain and dysfunction. Evaluating these alternatives ensures that treatment is directed at the correct underlying issue, rather than merely addressing symptoms.
Key considerations in differential diagnosis include:
- Evaluating the nature of pain (acute vs chronic)
- Considering the patient’s medical history and lifestyle factors
- Performing a thorough examination to reveal specific characteristics of pain
Incorporating a comprehensive and detailed approach to diagnosis can increase the efficacy of the treatment strategy, ultimately benefitting patient outcomes. Effective communication of these diagnostic processes among healthcare practitioners is also vital, as it fosters a cohesive understanding of cases and promotes collaborative treatment strategies.
Treatment Options for Sacral Dysfunction
In addressing sacral dysfunction, it is crucial to explore relevant treatment options that provide relief and management strategies. These treatments can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition. Importance lies in tailoring these treatments to the individual's specific symptoms and underlying causes, thereby optimizing the outcomes. Multiple modalities are applicable, including physical therapy, pharmacologic interventions, and surgical options. Each method presents its own benefits and considerations which must be understood by both practitioners and patients alike.
Physical Therapy Interventions
Physical therapy plays a fundamental role in the management of sacral dysfunction. This approach generally emphasizes movement re-education, muscle strengthening, and coordination.
Physical therapists may utilize manual therapy techniques, which include mobilizations and manipulations aimed at restoring normal function to the sacral region. These techniques can help reduce pain and enhance range of motion. Rehabilitation exercises such as stretching and strengthening are also essential components designed to support pelvic stability.
Benefits of physical therapy include:
- Pain alleviation through targeted interventions
- Improved mobility by increasing strength and flexibility
- Enhanced body awareness, which can prevent future issues
However, practical considerations need to be recognized. Individual results may vary based on the severity of the dysfunction and adherence to the prescribed exercise regimen. Additionally, patient education on posture and movement mechanics can further support therapy outcomes.
Pharmacological Treatments
Pharmacological treatments may complement physical therapy in managing sacral dysfunction. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen or naproxen, are often prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In some cases, stronger pain medications might be suggested based on the severity of the symptoms.
Moreover, muscle relaxants can help ease tension in surrounding muscles, promoting greater comfort. The use of nerve pain medications, such as gabapentin, can also be considered, especially in cases where neurological symptoms arise.
Points to consider within pharmacology include:
- Dosage and duration of medication use to minimize side effects
- Monitoring for interactions with other drugs
- Follow-up consultations to assess the effectiveness of treatment
Notably, relying solely on medication without accompanying physical therapy may not provide a long-term resolution for underlying dysfunction.
Surgical Considerations
In certain cases of sacral dysfunction, surgical options might become necessary. Procedures may be considered when conservative treatments fail to yield adequate results or when dealing with structural issues that critically impact functionality.
Common surgical interventions could involve modifications to the sacrum or adjacent structures, addressing conditions like herniated discs or severe spinal deformities. Additionally, sacroiliac joint fusion might be indicated for chronic instability or pain.
Key considerations include:
- Risks versus benefits of surgical intervention
- Post-operative rehabilitation requirements for optimal recovery
- Long-term outcomes, which may vary significantly by procedure
It remains vital for healthcare professionals to conduct thorough evaluations, with appropriate imaging and assessments designed to inform surgical decisions.
It is essential to take a holistic approach when considering treatment options for sacral dysfunction. Integrating various modalities ensures that all aspects of the patient's condition are addressed effectively.
Understanding the full spectrum of treatment options adds great value to the management of sacral dysfunction. Each choice must be tailored, allowing individuals to regain their health and improve their livelihood.
The Role of Lifestyle in Managing Sacral Dysfunction
Lifestyle choices play a crucial role in managing sacral dysfunction. Understanding the everyday factors that can influence this condition enables patients to take actionable steps towards relief and improved function. The integration of lifestyle modifications is not merely an adjunct to other treatments but can often serve as a primary method for enhancing sacral health. By addressing both physical habits and environmental settings, individuals can foster a more supportive atmosphere for healing and prevention.
Exercise and Rehabilitation


Engaging in regular exercise is paramount for individuals dealing with sacral dysfunction. Tailored physical activity helps to strengthen the core muscles, which provide essential support to the sacral region. Low-impact exercises, such as swimming or cycling, allow for movement without placing excessive strain on the body. Moreover, rehabilitation programs often include stretching exercises that enhance flexibility and mitigate stiffness in the pelvic area.
The benefits of exercise extend beyond mere physical attributes. Enhanced circulation through movement can aid in nutrient delivery to damaged tissues, promoting faster recovery. Additionally, physical activity can serve as a buffer against the psychological burdens associated with chronic pain, thereby improving overall quality of life.
Important Points to Consider:
- Consult with a professional: Before starting an exercise regimen, consultation with a healthcare provider is essential. They can recommend specific exercises tailored to the individual's condition.
- Consistency is Key: Making exercise a regular part of daily life increases the likelihood of achieving positive outcomes.
- Listen to Your Body: It is imperative to stop any activity that exacerbates symptoms, allowing for modifications where necessary.
“Incorporating exercise can offer both physical and mental benefits, making it a cornerstone of managing sacral dysfunction.”
Ergonomic Adjustments
Ergonomic adjustments in the workplace and home environment can significantly impact the management of sacral dysfunction. Poor posture and improper body mechanics can aggravate sacral pain, making it crucial to establish supportive settings. Using ergonomic furniture, such as chairs that promote proper spinal alignment, can alleviate undue stress on the sacrum. Animation and proper desk setups also matter. Elevating a computer monitor to eye level reduces strain on the neck and back.
Additionally, practicing good body mechanics while lifting or moving objects is key to preventing further injury. Techniques like bending at the knees rather than the waist help maintain the integrity of the sacral region. Regular breaks and variation in positions can decrease the risk of sustained pressure on the lumbar and sacral areas.
Recommendations for Ergonomic Adjustments:
- Chair Height and Support: Choose a chair with adequate lumbar support, and adjust it to allow the feet to rest flat on the floor.
- Desk Setup: Ensure that the workspace encourages a neutral spine with the keyboard at a comfortable height.
- Monitor Position: The top of the monitor should be at or slightly below eye level, reducing neck strain.
Incorporating these lifestyle elements creates a holistic approach to managing sacral dysfunction. With thoughtful adjustments in daily routines and environments, individuals can experience a notable improvement in their condition.
Case Studies: Real-Life Insights
Case studies play a crucial role in understanding sacral dysfunction as they offer real-world examples that illustrate the complexities involved. By examining specific patient experiences, healthcare professionals can identify patterns and refine treatment approaches. These narratives allow for an in-depth look into the various symptoms, diagnostic processes, and responses to treatment that encompass the individual experience of sacral dysfunction. By focusing on these specific cases, readers can gain insights into the multidimensional effects of this dysfunction on patients' lives. Furthermore, case studies can highlight the importance of personalized care strategies and foster a deeper understanding of the sociocultural factors that may affect treatment outcomes.
Case Study One
This case study centers on a 45-year-old female patient who presented with chronic lower back pain that radiated to her legs. After several consultations, she was diagnosed with sacral dysfunction as a result of a combination of trauma and poor posture over the years. The process began with a clinical assessment that involved both physical examinations and imaging modalities.
Symptoms Observed:
- Persistent pain in the sacral region
- Tingling sensations in the legs
- Limited mobility causing difficulties in daily activities
Upon further investigation, it was determined that her symptoms were exacerbated by a sedentary lifestyle and the ergonomic setup of her workspace. A targeted physical therapy intervention was initiated, focusing on strengthening the pelvic girdle and correcting postural habits. Within weeks, significant improvements were noted, leading to increased mobility and decreased pain. The effective collaboration between healthcare providers and the patient's adherence to the rehabilitation program was key to her recovery.
Case Study Two
In the second case study, a 32-year-old male athlete presented with acute sacral pain after a minor accident during practice. Unlike the previous case, this patient displayed unique challenges due to his high level of physical activity. Despite the absence of significant trauma, diagnostic imaging revealed an alignment issue in the sacral region that was contributing to the pain.
Symptoms Present:
- Acute sharp pain during athletic activities
- Muscle weakness in the lower extremities
- Frequent episodes of instability while running
Following a comprehensive assessment, a customized intervention plan was created that included both physical therapy and modifications to his training regimen. The goal was to address the anatomical misalignment while preserving his athletic performance level. By integrating manual therapy techniques and sport-specific exercises, the patient was able to return to his prior activity level with minimal discomfort after three months of targeted rehabilitation.
Both case studies exemplify the diverse manifestations of sacral dysfunction and underscore the necessity for individualized treatment approaches. Understanding these unique patient journeys can enhance clinicians’ ability to diagnose and manage sacral dysfunction effectively.
Recent Research and Advances
Recent research in sacral dysfunction emphasizes its impact on overall health and well-being. As medical science evolves, new methodologies and insights are constantly reshaping our understanding. In this section, we consider recent advances highlighting the shifts in approaches from traditional methods to innovative ideas. Keeping abreast of these shifts can aid practitioners, researchers, and patients alike in managing sacral conditions more effectively.
Current Trends in Research
Current research trends focus on several pivotal areas of sacral dysfunction.
- Multidisciplinary Approaches: There is a growing recognition that treating sacral dysfunction requires collaboration across various fields. Physical therapy, osteopathy, and neurology are increasingly coming together to offer more effective treatment plans.
- Neurophysiological Insights: Researchers study the neurophysiological mechanisms that connect sacral dysfunction with pain syndromes. These insights lead to better understanding of how nerve pathways contribute to both pain and muscle control.
- Use of Technology: Advancements in technology, including imaging techniques such as MRI and CT scans, have enhanced diagnostic precision. This technology allows for a more nuanced understanding of sacral alignment and function, informing treatment strategies.
- Patient-Centered Outcomes: More studies focus on how sacral health impacts quality of life. The emergence of patient-centered research helps to identify what outcomes matter most to people suffering from sacral dysfunction.
Innovative Treatment Modalities
A shift towards innovative treatment modalities marks a significant advancement in managing sacral dysfunction. Some of these modalities include:
- Regenerative Medicine: Techniques such as platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy and stem cell injections are being explored. These methods aim to promote healing at the sacral level and reduce inflammation which may contribute to dysfunction.
- Telehealth: The rise of telehealth has provided patients access to remote consultations. This is especially critical for those in underserved areas or with mobility issues. It facilitates continuous care and monitoring.
- Mind-Body Techniques: Practices such as mindfulness and yoga are being integrated into therapy plans. These approaches have shown promise in alleviating symptoms by addressing the psychological components of pain.
- Personalized Rehabilitation: Tailoring exercise and rehabilitation programs to meet individual needs is becoming common practice. This personalization ensures that interventions are relevant to the specific presentation of sacral dysfunction.
Through understanding these advances, healthcare providers can enhance their practice and offer more effective treatments for patients dealing with sacral dysfunction. It is crucial to keep updated with these trends to provide the best care possible and contribute meaningfully to the field.
Finale
The conclusion of this article highlights the significance of understanding sacral dysfunction and its overarching impact on health. Sacral dysfunction is often an underappreciated topic in health discussions, yet its ramifications touch multiple aspects of bodily function and well-being.
Summation of Findings
Throughout the article, we have explored various dimensions of sacral dysfunction. The essential points include:
- Definition and Relevance: Sacral dysfunction encompasses a variety of conditions affecting the sacrum, crucial for stability and mobility.
- Anatomical Insights: The sacrum is part of the pelvic structure and connects to vital musculoskeletal systems.
- Physiological Connections: Neurophysiological integration with pelvic structures is significant for proper functioning.
- Causes and Symptoms: Understanding trauma, postural issues, and chronic conditions aids in recognizing symptoms like pain, impairment, and neurological effects.
- Diagnostic Approaches: Effective clinical assessments, imaging techniques, and differential diagnostics form cornerstone methodologies for appropriate diagnosis.
- Treatment Options: The array of treatments available from physical therapy to surgical procedures reflects the complexity of managing this condition.
- Lifestyle's Role: Adopting a proactive lifestyle approach, including exercise and ergonomics, enhances sacral health and management outcomes.
- Case Studies and Research: Real-life examples and ongoing studies underline the dynamic advances in our understanding of sacral dysfunction.
"Understanding the multifaceted nature of sacral dysfunction is key to effective treatment and overall health management."
Future Directions in Sacral Health Research
Future research should focus on an integrated view of sacral dysfunction, considering its interplay with other health conditions. Key directions may include:
- Longitudinal Studies: These can help elucidate the long-term effects of sacral dysfunction on overall health.
- Interdisciplinary Approaches: Collaboration between different fields, such as orthopedics, neurology, and physical therapy, can provide a more comprehensive understanding.
- Innovative Treatment Modalities: Continued innovation in treatment options and rehabilitation strategies can lead to better management practices.
- Patient-Reported Outcomes: Gathering data from patients about their experiences can guide future research and policy.
In summary, addressing sacral dysfunction comprehensively will not only enhance individual patient care but also contribute significantly to the broader health landscape. We must continue to explore this condition, ensuring that it receives the attention it rightly deserves.















